- Welcome to, we are a factory specializing in the production and manufacture of saw blades!
- WhatsApp:+85261041051 | Map
Role of Diamond Blades
Mastering Precision: The Role of Diamond Blades
In precision machining, the role of diamond blades is akin to a surgeon’s scalpel. As the hardest natural material, diamond blades effortlessly cut ceramics, glass, and brittle materials while achieving micron-level precision in high-value industries like semiconductors and optics, making them the unsung heroes of modern manufacturing.

1. Why Diamond Blades Set Industry Benchmarks
Traditional alloy blades often produce burred edges when cutting silicon carbide or carbon fiber composites due to rapid wear. The role of diamond blades shines through their Mohs hardness rating of 10. Monocrystalline diamond edges maintain exceptional longevity—an automotive parts manufacturer reported a 47% increase in turbine blade tool lifespan.
2. Precision Revolution: From Lab to Production
In 5G ceramic filter processing, the role of diamond blades becomes critical. Using laser welding to fix diamond particles onto substrates and nano-level grinding, a telecom equipment maker achieved ±0.002mm tolerances, boosting yield rates by 22%.
3. Multidimensional Applications
- Medical: Zirconia ceramic machining for artificial joints
- New Energy: Precision cutting of lithium battery electrodes
- Optics: Sapphire lens polishing
These applications demonstrate how the role of diamond blades permeates advanced manufacturing.
Technological Leap: Macro to Micro Evolution
The latest multi-layer composite diamond blades reduce vibration by 60% when cutting fiberglass-reinforced plastics through gradient material design, delivering smoother cuts and minimized material waste.
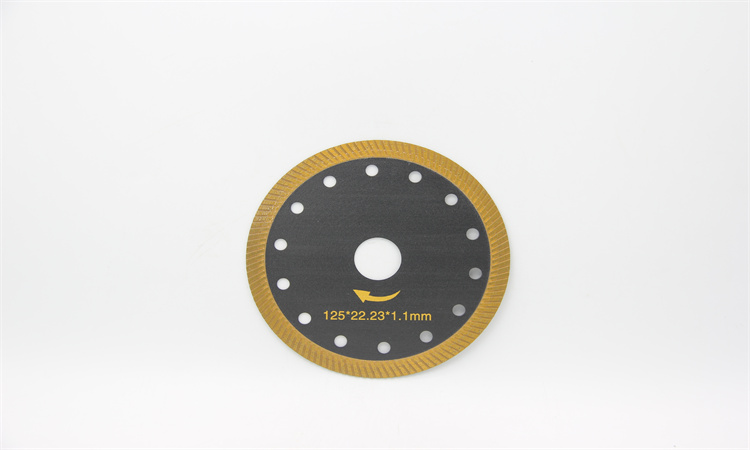

Q&A: Diamond Blade Essentials
Q: What distinguishes diamond blades from carbide blades?
A: Diamond’s hardness is 3-4 times greater than tungsten carbide, with superior heat resistance—ideal for cutting high-hardness composites.
Q: When should I replace a diamond blade?
A: Visible surface striations or sudden increases in cutting force indicate it’s time for microscopic edge inspection.
Q: Can diamond blades be resharpened?
A: Specialized vendors can perform limited-edge repairs using laser systems while preserving geometric accuracy.
Zhanyuetool
Shandong Zhan Yue Tools Co.
Site Search
Product Center
Testimonials
Contact Us
© 2025. All Rights Reserved.